Since the discovery of rubber in 1735 by a French scientist Charles de la Condamine, engineers have been fascinated by its properties and how it can be used. Today the field is even more complicated with a broader range of elastomers from which engineers can choose. Some are fully or partially vulcanized (cross-linked) as in the case with Thermoplastic Vulcanizates (TPV) or not, such as other Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE’s). Many different chemistries abound some of which include natural rubber (NR), styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), nitrile rubber (NBR), butyl rubber (BR), EPDM, neoprene, silicone, fluorinated elastomers, SEBS/SEPS, EVA, TPU, COPE, f-PVC, and COPA to name a few. How do you decide what to select? One of the key properties to differentiate among the various elastomeric materials is the ability for the material to be compressed and rebound, measured using a simple test, referred to as “compression set”. In simple terms, we can think of compression set, sometimes also referred to as “permanent set”, as an indication of the elastic memory of the material to return to its original state after deformation under a compressive force for a set time and temperature.
What is a compression set test?
Compression set is a test that measures rebound for the characterization of a material that is compressed for a prolonged time and temperature based on recognized industry standards. Often the degree of compression set (permanent set) is used to determine the elastomeric sealing capabilities of a seal against a surface in either dynamic, semi-dynamic, or static type application. The test is most commonly performed at 22, 70 or 168 hours on elastomer specimens of a given size and tested across various temperatures, for example, 70C, 100C, and 125C depending on the application requirements of the part. Although compression set doesn’t always directly correlate to part performance, it is a good starting point and a simple property to measure during development. It should be used in combination with the other stresses expected to be applied to the part including how the part is compressed vs deflected, how long it is deformed, how long it is stressed and relaxed, how fast the force is applied, and at what temperature fluctuations.
How is a compression set test performed?
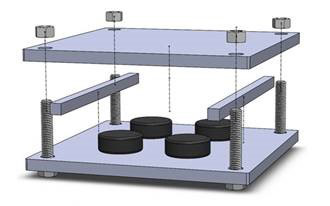
There are multiple test methods that are used in the industry; ISO 815 and ASTM D395 are the most commonly used. However, there are other test methods that may be used depending on the application and specifics on what the engineer is trying to achieve, as in the case of using ISO 1653 for testing compression set at low temperatures. Below describes a summary of how the compression set is measured per ISO 815. The test consists of compressing a standard size button, (6.2 mm thick [0.24”]/13.0 mm [0.51”] diameter, or 12.4 mm [0.49”] thick/29.0 mm [1.15”] diameter) to 75% of its original height for a given amount of time at a certain temperature, and then measuring its height 30 minutes after unloading. The compression set test equipment (jig) is shown in the picture below.
The compression set, CS, is expressed with the following relationship.

What does the compression set data tell you about the material?
The elastic recovery performance of a material is primarily determined by the viscoelastic properties which are also seen by its behavior under constraint in stress-relaxation. Because the elastic recovery is a time-dependent property, its result will be affected by the initial speed of compression and by the residence time under strain; the longer the residence time under strain, the lower the speed of elastic recovery and the higher the compression set. A similar effect happens with temperature. At higher temperatures, internally the polymer molecules move faster which lets stresses drop as the molecules slide more quickly past each other. So for equal lengths of time, the higher temperature will have greater stress relaxation and also a higher degree of compression set. Compression set can be used in many different ways. At the beginning of a project, it is used to screen materials and determine which is best for the application. It should be noted that part design can influence sealing capability, and should be considered along with the compression set of the material for optimum sealing performance. Once a material has been selected, it then can be used to monitor quality.
In summary...
Compression set data is useful on a relative basis and a good way to screen elastomeric materials to determine which might be best in your application. The permanent set of the material is an indication of the elastic memory of the material to return to its original state after deformation under a compressive force for a set time and temperature. Therefore, the higher the compression set, the lower the elastic recovery of the material.
